Fischer-Tropsch synthesis is a chemical process in which a mixture of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H₂), commonly referred to as synthesis gas, is converted into various hydrocarbon compounds of different chain lengths. Components that are liquid at room temperature can be used as fuels, while solid components can be used as waxes.
Learn more
An electrolyser is a device or system that uses the process of electrolysis to split water (H₂O) into its components hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) using an electric current.
Learn more
Methane pyrolysis is a chemical process in which methane (CH4), the main component of natural gas, is broken down into its components hydrogen (H₂) and solid carbon at high temperatures
Learn more
Hydrogenation is a chemical process in which hydrogen molecules (H₂) are added to unsaturated compounds, usually in the presence of a catalyst, to produce saturated compounds.
Learn more
The term "renewable raw materials" in the context of e-fuels (electric fuels or synthetic fuels) refers to sustainable and non-fossil carbon sources that are used as feedstock for the production of synthetic hydrocarbon fuels through a combination with renewable electricity.
Learn more
The term "carbon neutrality" in the context of e-fuels refers to the fact that the total carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions generated during the entire life cycle of the production, use and ultimate consumption of e-fuels are offset by a corresponding amount of CO₂ that is removed from the atmosphere or prevented from being released in order to produce the e-fuels.
Learn more
Both technologies offer unique advantages and challenges and are shaping the energy landscape in different ways.
Learn more
E-fuels have emerged as a potential solution for energy storage, for solving the temporal and local difference between renewable energy production and its consumption, and for the seamless continued use of existing means of transportation and logistics infrastructure. In terms of sustainability, e-fuels therefore offer a unique mix of ecological, social and economic benefits.
Learn more
Decarbonization is a complex and compelling process that aims to reduce the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO₂) and other greenhouse gases (GHG) in the atmosphere.
Learn more
A carbon footprint is a measure of the total amount of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide (CO₂), and other related emissions that are directly or indirectly associated with a person, organization, event, product or activity.
Learn more
E-fuel blending refers to the mixing of synthetic fuels, also known as electric fuels or e-fuels, with conventional fossil fuels in order to reduce the carbon emissions of the overall fuel mixture.
Learn more
Renewable energy is energy that is obtained from naturally occurring and renewable sources that are not depleted during use. These sources include sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, geothermal heat and biomass.
Learn more
Synthesis gas is an important gas mixture that consists mainly of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H₂) and, as the name suggests, is used for syntheses. It is traditionally produced using various processes in which carbon-containing starting materials such as fossil fuels, biomass or waste materials are converted into a gas mixture. Synthesis gas is produced from H₂ and CO₂ in connection with power-to-liquid or for the production of e-fuels.
Learn more
Synthetic kerosene is a fuel produced from hydrocarbons derived from renewable resources or carbon dioxide and hydrogen.
Learn more
Synthetic gasoline is a fuel made from hydrocarbons produced from renewable resources or carbon dioxide and hydrogen.
Learn more
Synthetic fuel is a combustible or fuel made from carbon and hydrogen molecules that are brought together in a chemical process.
Learn more
Synthetic diesel is a type of fuel that consists of synthetically produced hydrocarbons and is an alternative to conventional diesel.
Learn more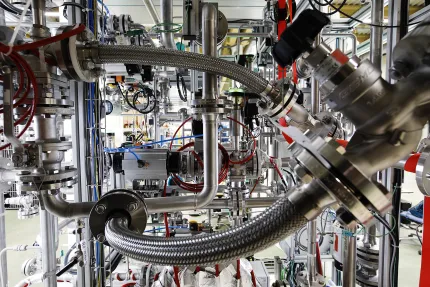
Power-to-liquid (PtL) is a process in which electricity generated from renewable sources is used to produce hydrogen by means of electrolysis.
Learn more
Methanol is mainly produced through methanol synthesis, in which carbon monoxide and hydrogen react at high temperatures and pressures.
Learn more
Emissions trading (ETS) is a climate policy instrument in which companies receive a limited quota of emission allowances that they can trade with each other.
Learn more
Alternative fuels for gasoline engines are synthetic or artificial fuels that can serve as a substitute for conventional gasoline.
Learn more
Alternative fuels for ships include a range of fuels that can be used as a substitute for conventional heavy fuel oil.
Learn more
Alternative fuels for aircraft include synthetic fuels produced from renewable resources or carbon dioxide and hydrogen.
Learn more
Alternative fuels are fuels that can be used as a substitute for fossil fuels such as petrol, diesel and kerosene.
Learn more
Hydrogen and e-fuels are both capable of enabling CO₂-neutral mobility.
Learn more
The BaWü project "reFuels" is a research initiative of the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology and its partners that focuses on the efficient production and use of regenerative fuels such as e-fuels.
Learn more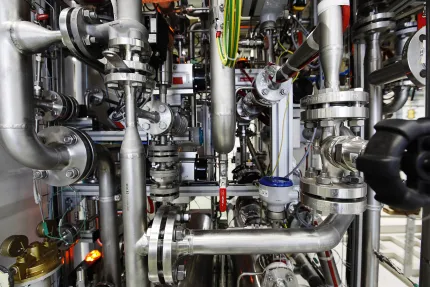
The production of e-fuels involves the conversion of renewable electricity into liquid fuels through electrolysis and chemical reactions with CO2.
Learn more
DIN EN 15940 is a specification for kerosene fuels, including diesel, produced from biomass.
Learn more
E-fuels, also known as synthetic fuels, are liquid fuels produced from renewable energy sources such as wind or solar energy.
Learn more
ASTM D1655 is an internationally recognized standard that relates to the testing and specification of Hydrotreated Renewable Jet (HRJ) fuels.
Learn more
Ultra-low carbon fuels (ULCFs) are fuels that produce significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions over their entire life cycle compared to conventional fossil fuels. These fuels are derived from renewable resources or sustainable processes and are often seen as a key solution to reducing CO₂ emissions in hard-to-decarbonize sectors such as transportation, aviation and shipping.
Learn more
RFNBO stands for Renewable Fuels of Non-Biological Origin. RFNBOs are climate-friendly energy sources that are produced without the use of fossil or biological raw materials. RFNBOs are based on renewable energy sources, in particular green hydrogen and carbon dioxide (CO₂), which is captured from the air or industrial processes. They are often seen as a promising solution for decarbonizing industry and the transport sector, especially in areas that are difficult to electrify directly.
Learn more
The Mass Balancing Approach is a method for certifying and tracking sustainable materials that are mixed with conventional raw materials in production processes. This approach makes it possible to track how much of a particular raw material - such as bio-based or recycled materials - is incorporated into the final product in a production facility without physically separating these raw materials from the rest of the production. The mass balance approach is often used in the plastics, chemical and energy industries to promote the integration of sustainable raw materials and transparently show their share along the supply chain.
Learn more
The Mass Balancing Approach is a method for certifying and tracking sustainable materials that are mixed with conventional raw materials in production processes. This approach makes it possible to track how much of a particular raw material - such as bio-based or recycled materials - is incorporated into the final product in a production facility without physically separating these raw materials from the rest of the production. The mass balance approach is often used in the plastics, chemical and energy industries to promote the integration of sustainable raw materials and transparently show their share along the supply chain.
Learn more
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a method for systematically evaluating the environmental impact of a product, process or service throughout its entire life cycle. The analysis covers all phases - from raw material extraction, production and use through to disposal or recycling. The aim of the LCA is to understand the ecological footprint of a product and to identify optimization potential for a more sustainable design.
Learn more
Aviation fuel, also known as kerosene, is the special fuel used to refuel aircraft. Aviation fuels are formulated to withstand the extreme demands of flight operations - high energy efficiency, stable combustion and temperature resistance at extreme altitudes and speeds. The most common type of aviation fuel is Jet A-1, which is used in turbine and jet engines.
Learn more
Aviation fuel, also known as kerosene, is the special fuel used to refuel aircraft. Aviation fuels are formulated to withstand the extreme demands of flight operations - high energy efficiency, stable combustion and temperature resistance at extreme altitudes and speeds. The most common type of aviation fuel is Jet A-1, which is used in turbine and jet engines.
Learn more
The Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) is a global organization that supports companies and financial institutions in setting and implementing science-based climate targets.The aim of the initiative is to bring the private sector into line with the requirements of the Paris Climate Agreement and to limit global warming to 1.5 °C. The SBTi enables companies to manage their emissions reductions in a targeted manner and make their progress transparent and verifiable.
Learn more
The Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHG Protocol) is an internationally recognized standard for the accounting and reporting of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. It was developed to provide companies, organizations and governments with uniform guidelines for measuring and managing their CO₂ emissions. The GHG Protocol is a joint initiative of the World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) and serves as the basis for many global climate protection initiatives, including the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi).
Learn more